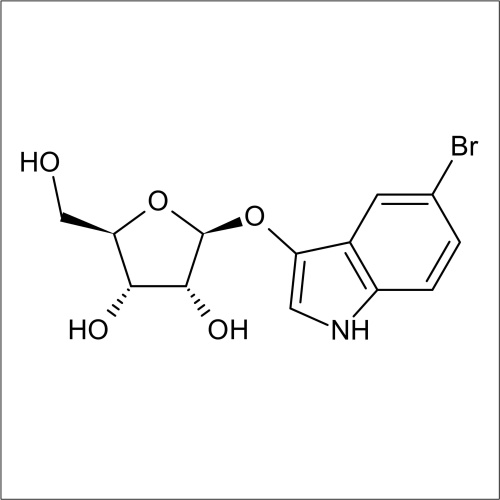
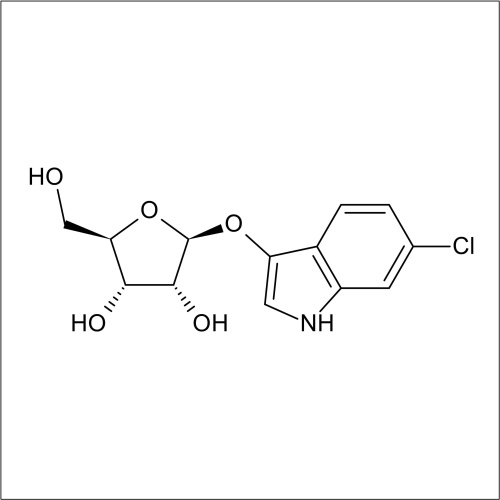
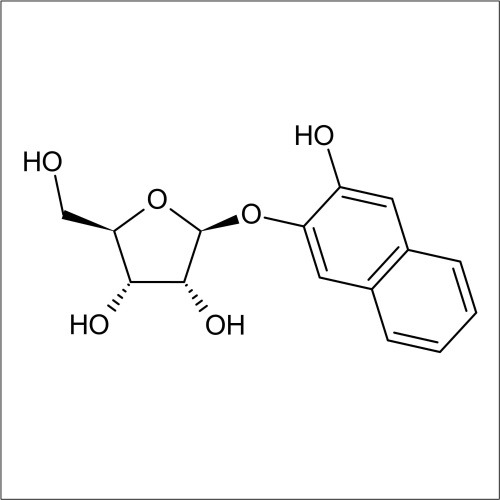
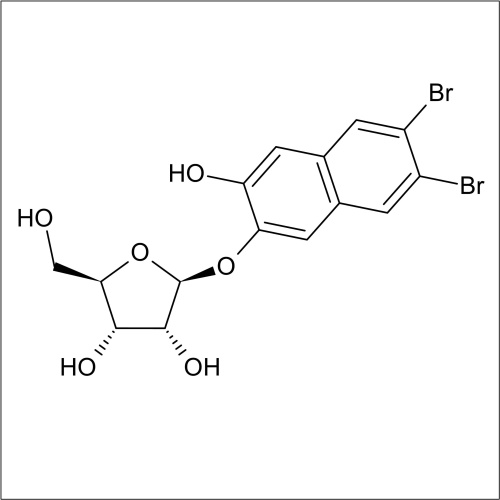
Beta-D-ribofuranosidase activity
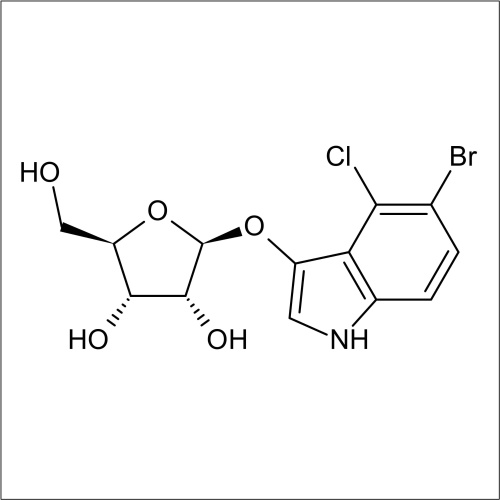
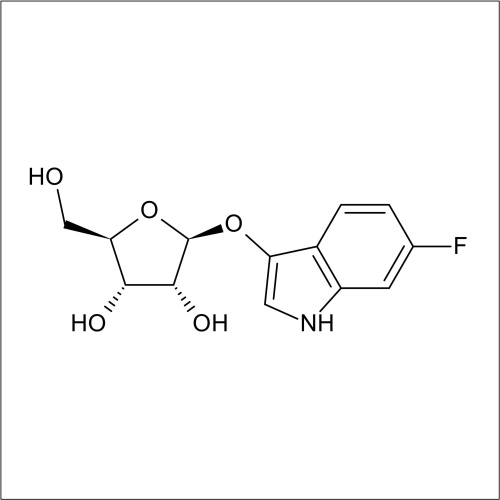
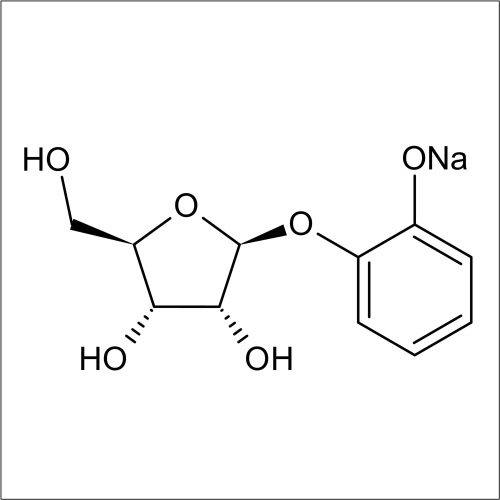
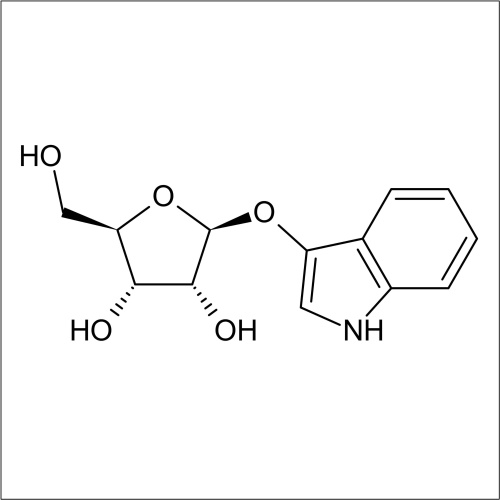
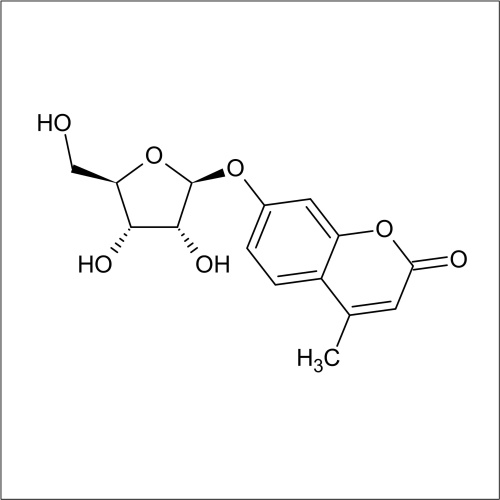
In recent years substrates for the detection of bacteria that express β-D-ribofuranosidase activity have been developed. In a collaboration between Professor John Perry co-workers at Freeman Hospital and Glycosynth 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl β-D-ribofuranoside (X β-D-riboside) (Product code 70180) and other novel chromogenic β-D-ribofuranosides were developed. β-D-ribofuranosidase substrates showed potential for the detection of certain bacteria; including Yersinia, Shigella, Vibrio, Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Arcanobacterium haemolyticum. β-D-ribofuranosides have also been reportedly useful for the identification of pathogenic S. aureus, including MRSA. Catechol β-D-ribofuranoside (Product code 14180) is an effective substrate, showing 100 % sensitivity for MRSA and MSSA after 18 h incubation in liquid media. Beta-D-ribosidase substrates have been shown to have an application for differentiating between Y. enteroclitica which does not hydrolyse these substrates.